System Name and Class Viewpoint
Description
This viewpoint provides the instructions to create the System Name and Class View in a System Description.
The initial steps for creating a system description are:
- Identifying the name of the system-of-interest.
- Identifying any base classifier and any of its properties that this system-of-interest inherits.
In addition, this section can provide any other system level definitions or concepts used across the whole system.
Rationale
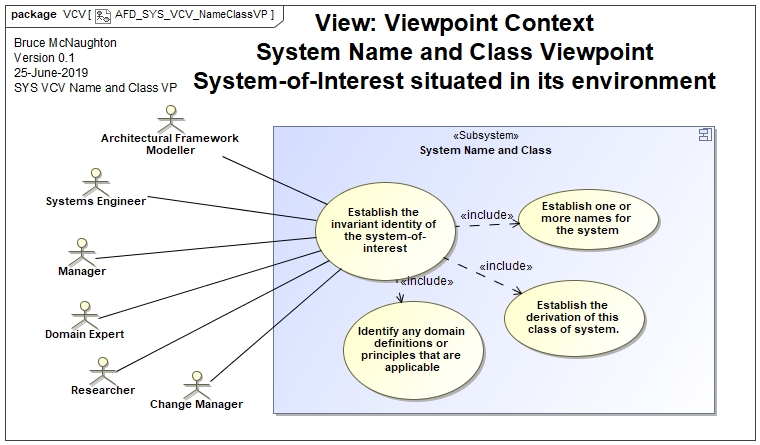
This view is critical to establishing the identity of a system-of-interest. Key elements of the identity are:
- Name
- Identified base classifier for the system-of-interest
- inherited definitions from other system descriptions
Stakeholders and their Concerns
Ontology Concepts and System Descriptions
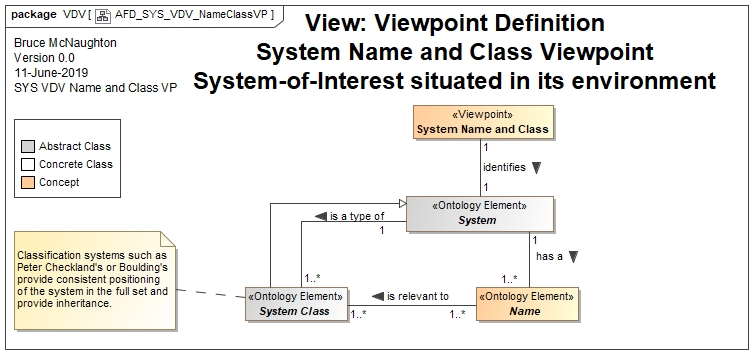
Models
The Name can be created as a single class in a class model
The Generalization links to other base classifiers is a critical aspect of creating the identity of the system-of-interest. Here are some examples of Base Classifiers:
- System (Abstract)
- Social System (Abstract)
- Designed Physical System (Abstract)
Link to the Top System Classifications PDF
The class model may also contain the generalizations to the identified 'based on' classes.
A UML Class model is optional for this view. The simple model is implied in the elements that are captured in this section. This viewpoint may also have a legend specification (text based view).
Steps to Create the View
- Identify the names or possible synonyms
- Identify the base classes that this system can be derived from.
- Optional: Create a Class diagram for this section to show the relationship of the system to other base classifiers. (or update the top system classification model).
Correspondences
- Any of the inherited elements from the base classes should be visible within the system description.
Examples
See the Household System Description as an example of a System Description that inherits a number of the basic structures and elements from the abstract class: Social System.
T.B.D. Links to be provided to example System DescriptionsSources
UML Classes and Generalization Associations.
Notes
Though a UML model may not be required in this section